ISO standards ESG are increasingly used as a practical foundation for accountability, risk management and management decision-making. Many companies can set targets, but the real value lies in how well those targets can be measured, tracked, and clearly explained over time.
This is where ISO standards come in. They do not replace reporting frameworks such as CSRD, ESRS, or GRI. Instead, they provide a solid process foundation that helps organise data and management practices in a consistent and verifiable way.
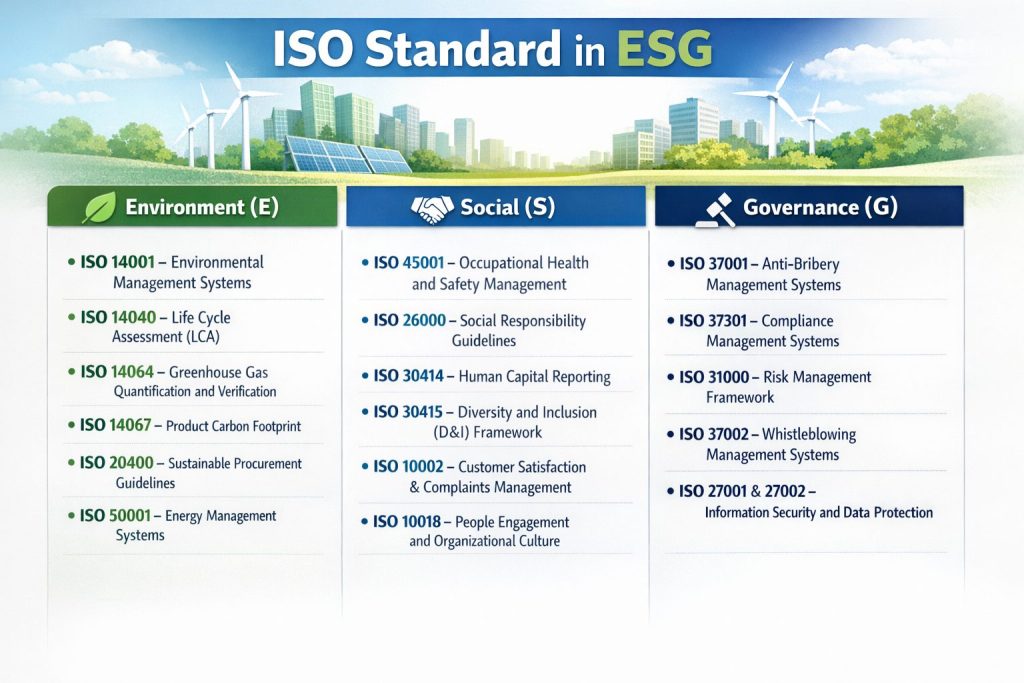
Environment (E)
- ISO 14001 – a structured approach to managing environmental aspects and risks.
- ISO 14040 – life cycle assessment (LCA) across the entire value chain.
- ISO 14064 – quantification and verification of greenhouse gas emissions at organisational level.
- ISO 14067 – a specific methodology for calculating product carbon footprints.
- ISO 20400 – guidance on sustainable procurement and responsible supply chain management.
- ISO 50001 – long-term management of energy efficiency.
Social (S)
- ISO 45001 – management of occupational health and safety.
- ISO 26000 – a reference framework for social responsibility and ethical business conduct.
- ISO 30414 – a structured approach to human capital reporting.
- ISO 30415 – a framework for promoting diversity and inclusion (D&I).
- ISO 10002 – management of customer satisfaction and feedback.
- ISO 10018 – guidance on people engagement and organisational culture.
Governance (G)
- ISO 37001 – policies and controls to prevent bribery and corruption.
- ISO 37301 – a systematic approach to legal and regulatory compliance.
- ISO 31000 – a strategic framework for identifying and assessing risks.
- ISO 37002 – international guidance for whistleblowing management systems.
- ISO 27001 & ISO 27002 – standards for managing information security and data protection.
What is the practical value of ISO standards ESG?
When ISO standards ESG are integrated into an ESG approach, they make it easier to move from general principles to working processes. This creates a stronger basis for audits, clearer communication with investors, and more informed management decisions.
In this sense, ISO standards are rarely a goal in themselves. They are tools that help ESG be applied consistently and in a way that makes sense in day-to-day business operations.
